Medical Chillers
How Do MRI Chiller Systems Work?
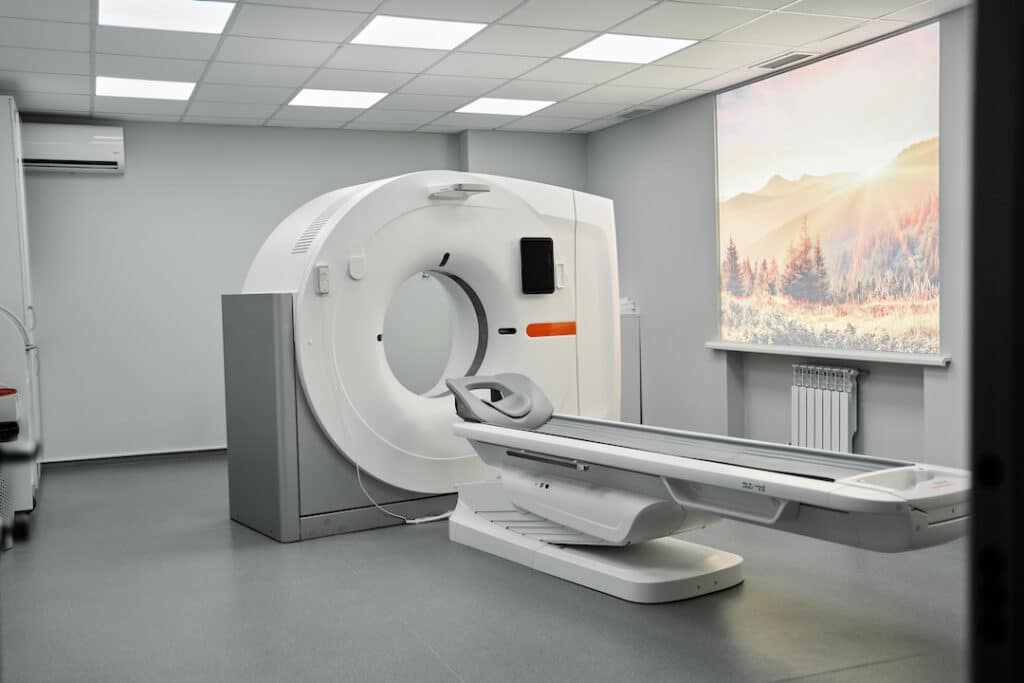
With the advancement of technology, especially in the medical field, we are constantly being introduced to new ways of imaging the human body to detect diseases. One of those primary tools has become an MRI or a Magnetic Resonance Imaging machine.
An MRI machine is a medical imaging procedure that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create detailed images of the inside of the body. MRIs are often used to diagnose medical conditions because they can provide clear images of everything from the brain to the heart.
Unlike other medical imaging procedures such as CT scans or X-rays, MRIs do not use radiation and are therefore considered safer. MRIs are also very effective in detecting soft tissue injuries.
During an MRI, the patient is placed inside a large cylindrical scanner. The scanner contains a powerful magnet that creates a magnetic field around the patient. This magnetic field causes the water molecules in the body to align themselves into a particular pattern.
Radio waves are then beamed at the body, they cause these water molecules to generate a small electric current. This current is picked up by sensors placed around the scanner, and the signals are processed by a computer to create an image of the inside of the body.
The images produced by an MRI can be very detailed and show everything from individual cells to entire organs. MRIs are often used to diagnose conditions such as tumors, blood clots, and other internal injuries. They can also be used to monitor the progress of a disease or the effectiveness of treatments.
MRIs are an important tool in the diagnosis and treatment of many medical conditions. Although the MRI was invented in 1977 and has therefore slipped into the cultural lingo, few people know or understand the importance of an MRI chiller system and how it works.
What is an MRI Chiller System?
An MRI Chiller is a piece of medical equipment used to keep the MRI machine cool. The chiller circulates water through coils inside the MRI machine to keep it at a consistent temperature. Without a chiller, the MRI machine would heat up and could be damaged.
MRI chillers are often located in a room adjacent to the MRI machine room. They are typically large, industrial machines that require a lot of space.
Do MRI Machines Need Chillers?
MRI machines use powerful magnets to create images of the body. These magnets are so strong that they can cause objects to become magnetized. For this reason, MRI machines must be kept in a very cold environment.
The typical MRI machine is kept at a temperature of -270 degrees Celsius. This is because the colder the environment, the less likely it is that any magnetic object will be affected by the MRI machine.
Some people may wonder if MRI machines need a chiller. The answer is yes. The chiller helps to maintain the temperature of the MRI machine and prevents it from becoming too warm. If the MRI machine becomes too warm, it can affect the quality of the images that are created. Additionally, if the machine gets too hot, it can be dangerous for the patients who are using it.
How Does an MRI Chiller Work?
MRI machine chillers work by circulating a refrigerant around a series of coils. As the refrigerant circulates, it absorbs heat from the MRI scanner. This process helps keep the scanner cool and prevents it from overheating. The cold refrigerant then passes through a condenser, which turns it back into a liquid. The liquid refrigerant is then circulated back to the MRI scanner to start the process over again.
What are the Benefits of MRI Chillers?
MRI chillers are an important part of maintaining the performance and safety of your MRI machines. Without them, the scanners could overheat and be damaged. MRI chillers also help reduce noise levels and improve image quality. Thanks to their many benefits, MRI chillers are an essential piece of equipment in any MRI scanner room.
What Types of Chillers are Used for MRIs?
There are three main types of chillers that are used for MRIs: water-cooled, air-cooled, and liquid nitrogen (LN2) cooled. The choice of chiller type depends on a number of factors, including the size and shape of the MRI machine, the climate where it will be located, and the electrical power available.
Water-Cooled
Water-cooled chillers are by far the most common type used in MRI machines. They can be either absorption or centrifugal chillers. Absorption chillers use ammonia as a refrigerant, while centrifugal chillers use Freon.
Air-Cooled
Air-cooled chillers are becoming more popular due to their lower cost and smaller size, but they can only be used in climates where the ambient air temperature is below 50 degrees Fahrenheit. This can be prohibitive if your office doesn’t have working air conditioning.
Liquid Nitrogen
LN2 MRI chillers are a type of medical refrigerator that uses liquid nitrogen to keep equipment cold. They are used in MRI machines to keep the magnets cooled down. Without an LN2 MRI chiller, the magnets would heat up and cause the machine to shut down. LN2 cooled chillers are used mostly in research machines where very low temperatures are required.
The choice of chiller type also affects the MRI machine’s operating cost. Water-cooled chillers use more energy than air-cooled or LN2 cooled chillers, but they are less expensive to purchase and maintain. Air-cooled chillers require more maintenance than water-cooled chillers because the fans need to be cleaned regularly to prevent dust from clogging them up. LN2 cooled machines have the highest running costs, but they also have the lowest capital costs.
It’s important to not only find an MRI chiller but to find the right one for your machine. Without an MRI chiller, you risk serious damage to patients and your machine. Save yourself some money and invest in one today!
If you want to learn more about MRI chillers, contact KKT Chillers.